What is Radiant Energy?
By Sydney Cohen – Radiant energy is the energy contained in the vibrationally charged particles around an object. It is a form of “electromagnetic energy,” that “can take the form of visible waves – which is what we call light energy – or invisible waves such as radio waves or x-rays.”
Different electromagnetic waves of the same nature are identified by their size and frequencies. Electromagnetic energy waves that are with low frequency and long wavelength are high energy waves. Those with low frequency and long wavelengths are low power waves.
Unlike light energy, that is reflected into the atmosphere by air where energy has the capability to work, radiant energy is transmitted into the atmosphere in the form of electromagnetic waves with electrical and magnetic properties.
Examples of Radiant Energy
An electromagnetic wave that scatters radioactive radiation can have many forms. Light waves are the only wavelengths we can typically see within our human sight.
Some examples of radiant energy include x-rays, radiant heat systems, and solar cells or solar panels that convert the energy of the sun into solar electricity. Further “examples of radiant energy include the warmth that radiates from a hot stove and the warmth from direct sunlight.”
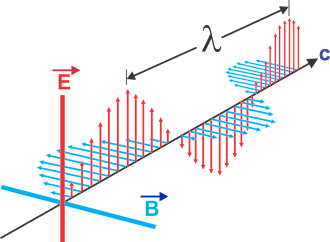
Electromagnetic Waves Carry Energy
Electromagnetic waves are similar to other waves like waves in an ocean, in that they have higher parts and lower parts and they move. All types of electromagnetic waves are defined by wavelengths which are usually the distance between waves.
Another way of looking at the different types of waves is based on their frequency which can be thought of as the speed at which the wave can move. Waves with long wavelengths have more power. The number of waves formed in a period of time can also be expressed in terms of hertz – which is the number of waves produced in a certain period.
The Connection Between Waves and Energy
Electromagnetic waves with shorter wavelengths and high frequency carry more energy. A wave with a higher frequency has more ability to do work and thus carry more energy.
Consider someone throwing a punch into a punch-bag: each hit can be seen as a wave. If the opponent punches faster the bag will move more. And that means more work will happen. Higher frequencies carry more radiation compared to faster wavelengths. Imagine each punch is the equivalent of an electromagnetic wave. This wave is equivalent to the energy in another wave. A wave has stronger energy.
Radiant Energy and Religion
According to an article entitled Development of Knowledge of Radiant Energy as Applied to Medical Uses, “Primitive man evidently had some sort of idea of the importance of sunlight—the only form of radiant energy he recognized—in human health and welfare, for all primitive religions contained some element of sun worship”.
Other forms of radiant energy are recognized by humans only by the effects they have, such as radiation, but the sun has offered visible radiant energy that has influenced every culture in the world for centuries.
Ancient Relationships with Radiant Energy
The website Healing Earth explains different cultures’ relationship with the sun:
- Ancient Egyptians honored a sun god named Ra. Egyptian temples were built with openings at the top so that the sacred rays of the sun could beam down upon the ritual altar and provide spiritual energy for the prayers and sacrifices performed there.
- The Ancient Greeks also honored a sun god, called Helios. In his poetry, Homer, (8th century BCE), described how Helios began and ended each day by driving a chariot of four-winged stallions across the sky.
- For many Indigenous People in the Northern Hemisphere, rituals related to sun worship traditionally occur in June, at the time of the summer solstice, (the longest day of the year). The Iroquois and Sioux Native Americans, in particular, recognize the sun as a life-giving force. Each year members of these nations perform the Sun Dance which reestablishes the bond between themselves, the Earth, the sun, and the energies of the new growing season.
Understanding Radiant Energy
In conclusion, radiant energy is a type of electromagnetic radiation. It can be emitted by certain materials, such as glass and metal, when heated up.
When the radiant energy is absorbed it creates heat which may produce light or other types of thermal effects like heating objects around it. It is important to know the science behind radiant energy, as it is present in our everyday lives.
* Featured image source