By Abby Rabinowitz
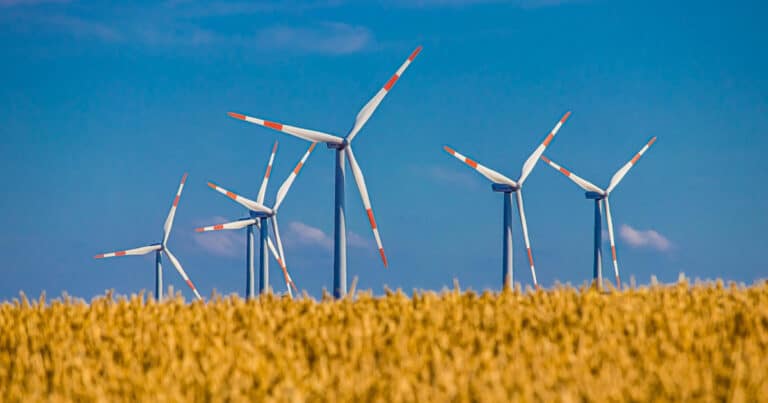
Wind power is a clean, commonly used source of renewable energy.
Wind turbines use energy captured from the wind and converts it into usable electrical energy.
Wind farms are collections of turbines that generate large quantities of electricity without emitting any pollutants or greenhouse gases into the air, making them a clean alternative to other power sources.
The Capacity of Wind Turbines
Wind turbines are typically around 79 meters (260 feet) high. The top section of each turbine, known as the nacelle, rotates so that the blades in the wind face the turbine.
Currently, there are over 60,000 wind turbines in the United States alone. Those turbines have a combined output of 105,583 megawatts. That is enough energy to power over 31 million houses!
Wind turbines work using an 18 foot rotor which allows for the generation of around 8,000 kWh of electric power when powered by winds of approximately 12 miles per hour. According to the Wind Energy Foundation, a single turbine of this size can produce nearly 100% of the electricity needed for an average American home.
Modern Wind Turbines
There are various types of wind turbines used to generate renewable energy.
Vertical axis turbines are available in numerous types however most commonly seen in the Darrius model. These turbines are omnidirectional, or facing in all directions, so the turbine can produce energy without being turned to face the wind.
Horizontal axis turbines can be recognized by their three main blades. These blades can be moved in order to face the wind and maximize their efficiency. They are used more commonly than Vertical axis turbines.
Wind Becomes Electricity
So, how does wind energy work? On wind farms, turbines spin and use wind to convert the energy found in the wind into electrical energy. The process starts when wind turns a rotor on top of a tower and force the blades to spin. The spinning blades power an electrical generator that produces electricity, which in turn forms usable power from the kinetic energy in the wind.
Generating Electricity From Kinetic Wind Energy
In order to create electricity from wind energy there are two key components required. The first is a generator or turbine that uses the kinetic energy of moving air which spins a rotor. The second is an electric power converter or alternator which transforms the rotor’s kinetic energy into a usable electrical current.
Wind Speed
Wind turbines come with either one-bladed rotating devices called propellers or multiple bladed rotors on shafts. The blades catch the wind and can rotate at speeds of up to 320 km/hour . This force causes the blades to push against the spinning mass, like a lever pushing against a fulcrum, generating torque proportional to both speed and area swept per revolution by each rotor blade.
In order to generate energy for the power grid, it takes a 10-20 RPM (revolutions per minute) of speed. As a result, turbine blades are built with a calculated curve in order for their surfaces to capture as much wind as possible. The wind’s kinetic energy can spin a central shaft turning which turns a drive shaft.
Does Wind Power Need Wind?
Some people worry that wind power is limited because wind levels are unpredictable. In times of minimal wind, the power generated can vary and prove to be inadequate, resulting in blackouts. However, in order to combat this, wind turbines are typically coupled with traditional fossil fuel energy sources such as oil, gas, or coal.
In addition, when used on a large scale, wind turbines are often spread out over many different locations, resulting in a lattice configuration that diversifies a customer’s exposure to wind across multiple locations. This diversification of regions helps guarantee a relatively steady supply of wind energy throughout the year.
Wind turbines are also typically built in regions with high wind levels on tall ground where wind speeds are greater. Before people invest in wind farms, there are often multiple studies and a search conducted in order to find the best possible place for a wind farm. This maximizes the efficiency of those wind farms and their ability to capture more energy from the passing air currents.
Wind Energy: On The Land and In The Sea
Wind turbines can be used either on land or offshore in order to generate electricity, which is then delivered through power lines to homes and businesses near the source. While historically land based wind farms have been more popular, more recently, offshore windfarms have gained in popularity.
Off shore windfarms are located over water where the offshore wind tends to blow faster and more consistently than on land, resulting in fewer interruptions. However, most wind farms are currently located on land, and use onshore wind to power the turbines.
Storing Wind Energy
In addition to pairing wind energy with fossil fuels and strategically positioning wind turbines to ensure a constant supply of wind energy, the national department of energy and scientists are also exploring ways to efficiently store wind energy.
New research findings show that in the future, electric batteries, such as lithium car batteries, may be used to store the energy generated by the wind turbines. This would reduce the vulnerability of small turbines to wind fluctuations, enabling them to become a reliable, primary energy source.
During periods of heavy wind, excess wind, that is now wasted, would be stored enabling customers to utilize stored wind energy at times of low wind.
Our Future Using Wind Energy
As storage technology advances, it is likely that wind energy will become a pervasive clean, cost effective, power source that will allow for energy efficiency. Over 40 religious groups have already adopted wind power in their communities, will yours be next?
* Featured image source